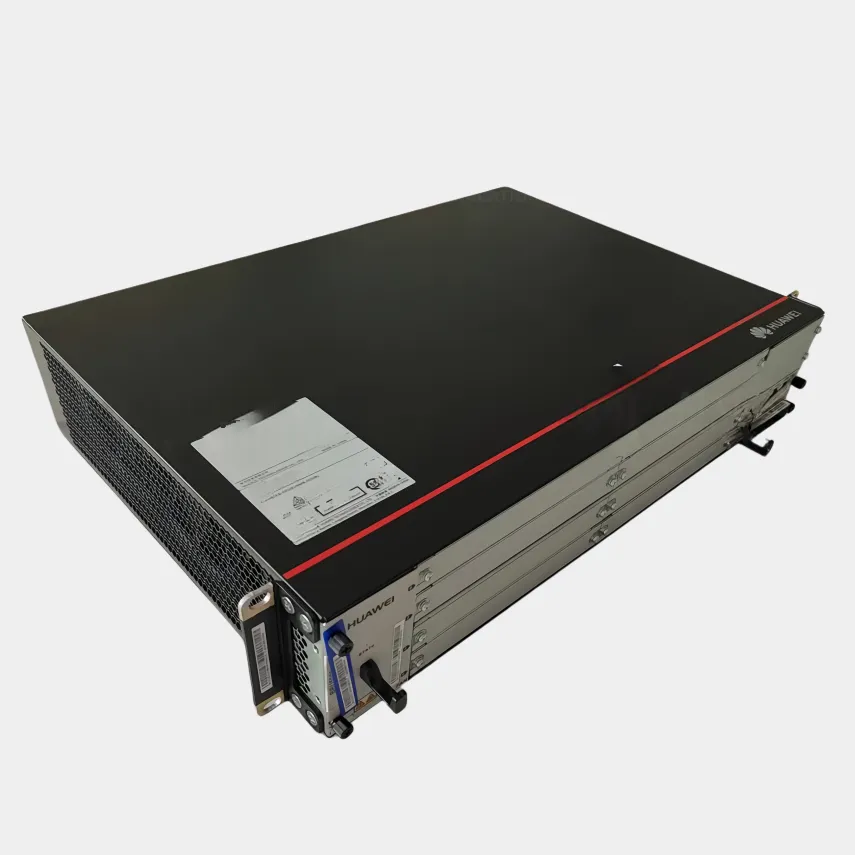
Baseband Unit (BBU) resource allocation refers to the dynamic or static distribution of processing capacity, memory, and radio interface resources within a BBU to optimize network performance, meet service level agreements (SLAs), and maximize resource utilization. In traditional BBUs, resources are often statically assigned to specific radio carriers or cells, leading to inefficiencies during traffic fluctuations underutilization during low traffic periods and congestion during peaks. Modern allocation strategies, however, leverage software defined and virtualized BBUs (vBBU) to enable dynamic resource sharing, where processing cores, memory blocks, and signal processing pipelines are reallocated in real time based on metrics like user count, data rate demands, and application type (e.g., prioritizing URLLC over eMBB). Key techniques include load balancing, which redistributes resources from overloaded cells to underutilized ones; QoS based allocation, which reserves resources for critical services (e.g., emergency calls, industrial IoT); and predictive allocation, using AI algorithms to forecast traffic spikes (e.g., sports events) and pre provision resources. Resource allocation must also account for fronthaul constraints ensuring allocated BBU capacity aligns with RRU (Remote Radio Unit) bandwidth and latency limits to avoid bottlenecks. In centralized BBU pools, allocation is further optimized across multiple sites, enabling cross cell resource sharing and interference coordination (e.g., coordinated multi point transmission). Challenges include minimizing reallocation latency (to avoid service disruptions) and balancing fairness (equal resource access across cells) with efficiency (maximizing throughput). Effective BBU resource allocation directly impacts network KPIs: reducing latency, increasing spectral efficiency, and lowering operational costs by minimizing idle resources, making it a critical component of modern 4G/5G network optimization.