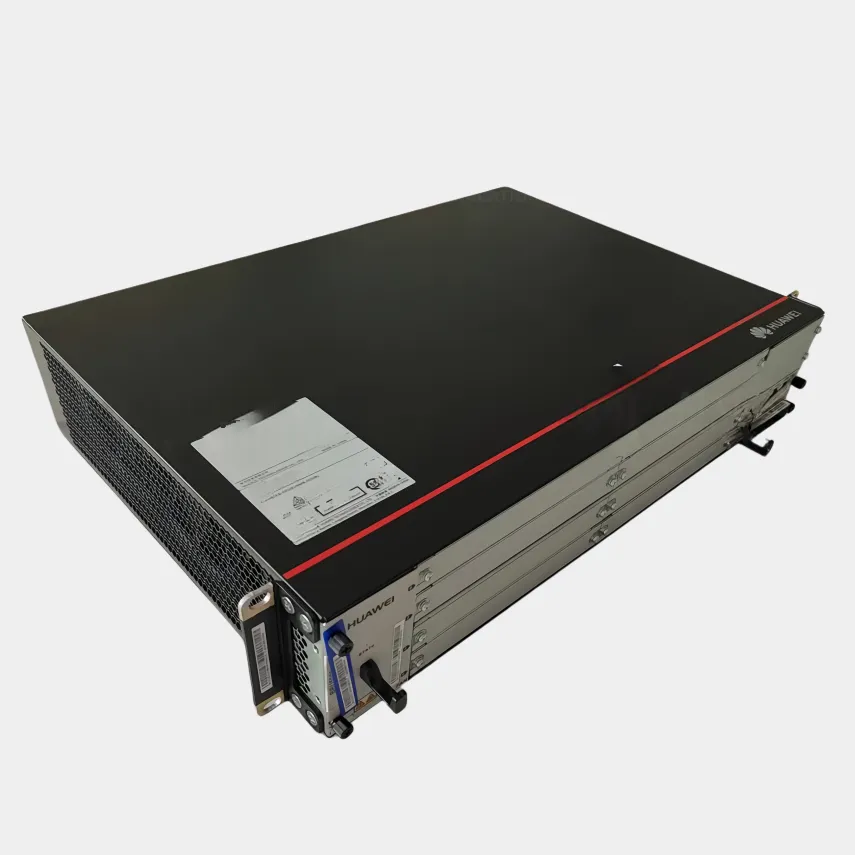
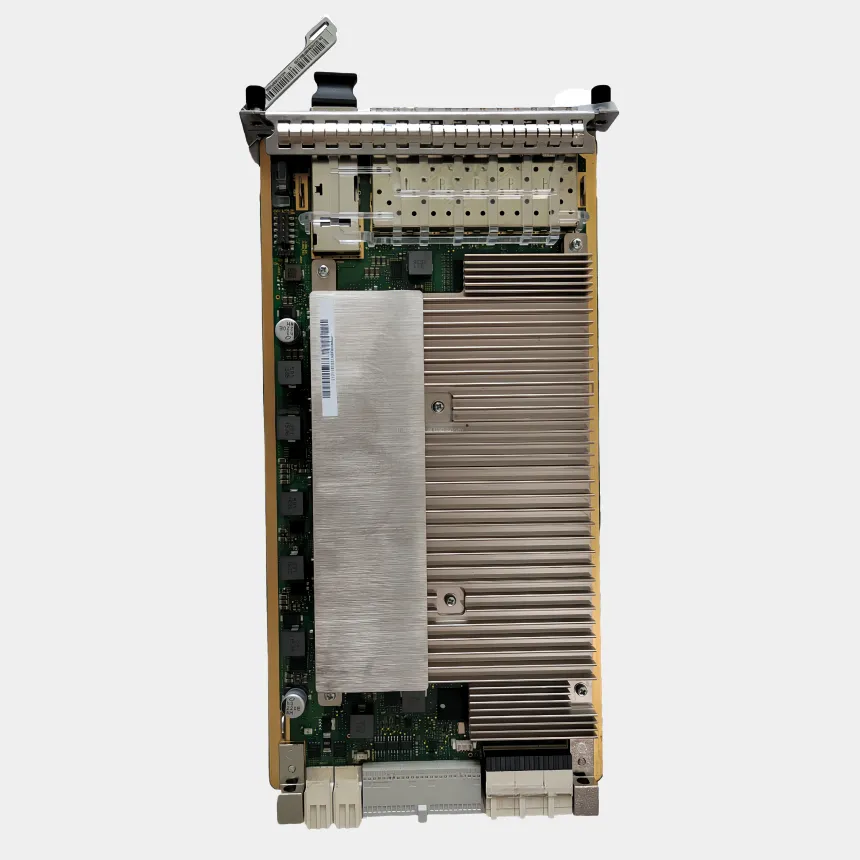
Virtualized baseband solutions, often referred to as vBBU (virtualized Baseband Unit), transform traditional hardware centric baseband processing into software defined functions running on commercial off the shelf (COTS) servers or cloud infrastructure, revolutionizing radio access network (RAN) flexibility and scalability. Built on Network Functions Virtualization (NFV) and Software Defined Networking (SDN) principles, these solutions decouple baseband processing from proprietary hardware, enabling deployment on general purpose servers, edge clouds, or data center infrastructure. This decoupling allows network operators to dynamically scale baseband capacity adding or removing virtualized instances (vBBU) via orchestration platforms (e.g., OpenStack, Kubernetes) to match traffic demands, eliminating the need for hardware upgrades. Key advantages include reduced capital expenditure (lower reliance on specialized hardware), faster service deployment (software updates instead of hardware swaps), and improved resource utilization (shared server infrastructure across multiple network functions). Virtualized baseband solutions also support multi vendor interoperability, breaking vendor lock in by standardizing interfaces (e.g., O RAN fronthaul specifications). However, challenges persist: maintaining real time processing capabilities (critical for 5G URLLC) on virtualized platforms requires optimized hypervisors and low latency networking, while ensuring signal processing performance matches dedicated hardware demands ongoing software optimization. Use cases span urban 5G networks, where dynamic scaling is critical, to edge computing deployments, where vBBUs can be hosted closer to end users to reduce latency. As the industry moves toward Open RAN, virtualized baseband solutions are becoming central, enabling operators to build more agile, cost effective, and future proof networks capable of adapting to emerging technologies like 6G and AI driven traffic management.