Core Functions of the Baseband Unit in 5G Signal Processing
Real-Time Signal Processing: Enabling Sub-10ms Latency in 5G Networks
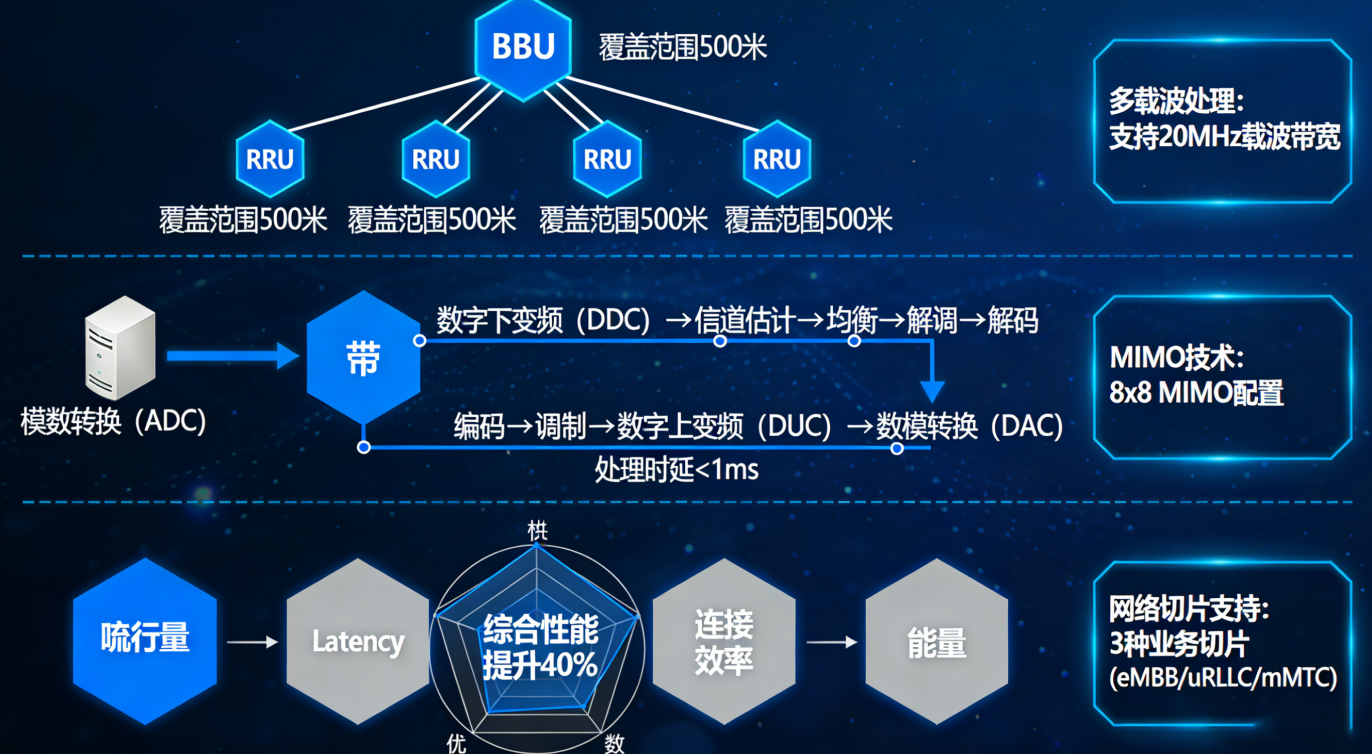
Baseband units handle critical digital signal processing tasks that need to happen within tight time windows, which makes them vital for achieving the super fast response times needed in 5G applications like self-driving cars and factory automation systems. These units complete their physical layer work in less than 2 milliseconds, keeping the total delay for signals going back and forth well under the 10 millisecond limit set by 3GPP standards. With techniques like parallel processing and special hardware boosts, BBUs can adjust their resource usage on the fly as conditions change. This means they keep running smoothly even when networks get really busy during rush hours or major events.
Digital Signal Pipeline: Modulation, Channel Coding, and MIMO Precoding
The BBU’s digital signal pipeline integrates three key functions to maximize signal integrity and spectral efficiency:
- Modulation using high-order schemes like QAM-256 and QAM-1024 encodes data into dense radio waveforms
- Channel coding with LDPC and Polar codes reduces bit error rates by up to 68% compared to 4G Turbo codes
-
MIMO precoding enables intelligent beam steering, improving spectral efficiency by 3.1x (Mobile Experts 2023)
Together, these processes minimize packet loss and sustain high throughput in densely populated urban environments.
Case Study: Top-Tier BBU Reduces Uplink Latency by 42% in Urban 5G Deployments
A 2023 field trial of a leading manufacturer’s BBU 6630 in Tokyo demonstrated significant performance gains through virtualization and machine learning-driven traffic prediction. The system achieved:
- 42% reduction in average uplink latency (from 9.2ms to 5.3ms)
- 17% improvement in cell-edge throughput
-
31% fewer dropped connections during handovers
These results confirm the BBU’s role as the computational core of reliable 5G networks, especially in high-density urban deployments.
BBU-Driven Network Performance: Latency Reduction, Throughput Scaling, and Efficiency
Centralized RAN (C-RAN): Dynamic Resource Pooling Through BBU Virtualization
Cloud RAN or C-RAN setups use virtual baseband units that pool processing power together for several cell sites instead of having separate boxes everywhere. What this does is get rid of those isolated hardware setups we used to see, cuts down on running expenses somewhere around 30 percent give or take, and makes it possible to shift workloads as needed in real time. When there's a sudden surge in network traffic, the system can actually grab spare capacity from nearby cells that aren't being fully utilized and send it where it's most needed. The result? Throughput goes up by nearly three times what it was before all this without needing to buy any new equipment. Pretty impressive when you think about it.
Massive MIMO Coordination and Spectral Reuse Enabled by Advanced BBU Control
Advanced BBU algorithms coordinate hundreds of antenna elements to deliver precise beamforming and spatial multiplexing. This allows multiple users to share the same frequency band simultaneously, boosting spectral efficiency by 47%. Directional signal focusing also minimizes interference, supporting 5x denser network deployments while maintaining 99.999% reliability—critical for mission-critical applications.
Key Impact:
- Latency reduction: Sub-10ms response for industrial IoT
- Throughput scaling: 40 Gbps per cell in mmWave deployments
- Energy efficiency: 60% lower power per gigabyte vs. distributed RAN
Key Hardware Components Powering Baseband Unit Performance
FPGA/ASIC Acceleration: Achieving Higher FFT Throughput vs. Legacy x86 Systems
Field Programmable Gate Arrays (FPGAs) along with Application Specific Integrated Circuits (ASICs) offer the kind of computing power needed for handling 5G signals in real time, beating older x86 systems when it comes to getting things done faster and using less energy overall. These special purpose chips really speed things up for tasks that can be processed simultaneously such as those Fast Fourier Transform calculations everyone talks about, which are pretty much necessary for getting modulation and demodulation right in these big MIMO setups we see everywhere now. When companies move away from regular CPUs and onto FPGA or ASIC solutions, they basically take all those heavy lifting operations off the main processor. This approach cuts down on processing delays while also saving quite a bit of electricity. Some studies show around a third to almost half reduction in power usage in city areas where these technologies get deployed.
Processor, DSP, Memory, and Interface Integration in Modern BBU Design
Today's baseband units pack a lot into one box these days - think multicore processors working alongside specialized digital signal processors, plenty of high speed memory, and all sorts of standard connections rolled into one neat package. The DSP does most of the heavy lifting when it comes to modulating signals, demodulating them back out, and handling those complicated channel coding tasks. Meanwhile, the regular processors take care of things like managing network slices and other upper level protocol stuff. For dealing with massive amounts of radio frequency data coming in, synchronous DRAM steps in as the buffer, handling speeds well over 200 gigabits per second which keeps everything from getting backed up during those inevitable traffic spikes. And speaking of connections, there are several important interfaces involved in making all this work smoothly together.
- eCPRI: Enables low-latency fronthaul connectivity
- 25GbE: Supports backhaul aggregation
-
PCIe Gen4: Facilitates high-speed inter-chip communication
This tightly integrated design eliminates bus contention, ensuring deterministic latency below 100µs for ultra-reliable applications.
Strategic Advantages of Baseband Units: Scalability, Energy Efficiency, and Futureproofing
O-RAN Trade-offs: Balancing Disaggregation and BBU Performance Consistency
The Open RAN concept actually encourages more vendors to enter the market and fosters innovation by separating hardware from software components. However, this approach creates problems when trying to keep baseband unit performance stable across different equipment. Modular systems do allow for easier scaling and expansion, plus they can cut energy consumption by around 30 percent according to the Telecom Efficiency Report from last year. But these benefits come at a cost. The system needs strict compliance with interface specifications otherwise there will be issues with signal timing variations and inconsistent data transfer rates. When dealing with applications where milliseconds matter, such as factory automation systems connected through IoT devices, network providers have no choice but to make sure everything works together seamlessly from start to finish. Deploying BBUs strategically means finding that sweet spot between what open platforms offer in terms of adaptability versus what's needed to meet the strict performance requirements of upcoming 5G-Advanced specs and even the still undefined 6G standards.